MELTING POINT: −7.3°C
BOILING POINT : 59°C
DENSITY : 3.12 g/cm 3 (liq. at 20°C)
MOST COMMON IONS : Br − , BrO − , BrO 3 − , BrO 4 −
Element Bromine - Br. Comprehensive data on the chemical element Bromine is provided on this page; including scores of properties, element names in many languages, most known nuclides of Bromine. Common chemical compounds are also provided for many elements. Bromine derives its name from the ancient Greek word for ‘Stench’ - Bromos. Much like Chlorine and Fluorine it has a strong smell. Bromine is a very reactive element and does not occur freely n nature but instead exists as white/colourless crystalline solids as halide salts. The number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in an electrically neutral atom, so there are 35 electrons in a bromine atom. How many bonds can bromine have? Bromine will normally form one covalent bond. Bromine, which belongs to group 17 and period four of the Periodic Table, has seven outer shell or valence electrons.
Bromine is a member of a family of elements known as halogens that are found in group 7A of the Periodic Table. Bromine was discovered in 1826 in Montpellier, France, by French chemist Antoine J. Balard.
Bromine is one of two elements (the other being mercury) that is liquid at normal temperatures. As with the other halogens, bromine is very reactive, corrosive, and poisonous. Both the liquid and vapor of bromine are deep red in color. Bromine has a pungent, irritating odor that is the source of the element's name (the Greek word bromos means 'stench').
Elemental bromine is a diatomic molecule (Br 2 ). Bromine will combine with most other elements. Reaction with metallic elements leads to salts such as silver bromide (AgBr), in which the bromine atom has a −1 charge and oxidation number. Bromine forms many interesting covalent compounds as well, including two oxides: bromine (IV) oxide (BrO 2 ) and bromine (I) oxide (Br 2 O).

Bromine is produced commercially from natural brines and from sea-water either by electrolysis or with displacement by chlorine, a somewhat more reactive halogen. The concentration of bromine in seawater is approximately 67 parts per million (ppm) by weight; it is found in Earth's crust at an average level of 3 ppm.
Bromine compounds have a variety of uses. Methyl bromide (CH 3 Br) is a common agricultural soil fumigant; other bromohalocarbon compounds have been used as refrigerants and fire suppressants. Inorganic bromides are important components of photographic emulsions. Bromine reacts with liquid water to produce hypobromite ion (BrO − ), a powerful bleaching agent. There are also many dyes and pharmaceutical agents that contain bromine.
SEE ALSO Halogens .
John Michael Nicovich
Bibliography
Lide, David R., ed. (2003). The CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics , 84th edition. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Internet Resources
Winter, Mark. 'Bromine.' The University of Sheffield and WebElements Ltd., U.K. Available from http://www.webelements.com .
Element Bromine - Br
Comprehensive data on the chemical element Bromine is provided on this page; including scores of properties, element names in many languages, most known nuclides of Bromine. Common chemical compounds are also provided for many elements. In addition technical terms are linked to their definitions and the menu contains links to related articles that are a great aid in one's studies.
Bromine Menu
- Bromine Page One
- Bromine Page Two
- Bromine Page Three
Overview of Bromine
- Atomic Number: 35
- Group: 17
- Period: 4
- Series: Halogens
Bromine's Name in Other Languages
- Latin: Bromum
- Czech: Brom
- Croatian: Brom
- French: Brome
- German: Brom - r
- Italian: Bromo
- Norwegian: Brom
- Portuguese: Bromo
- Russian: Бром
- Spanish: Bromo
- Swedish: Brom
Atomic Structure of Bromine
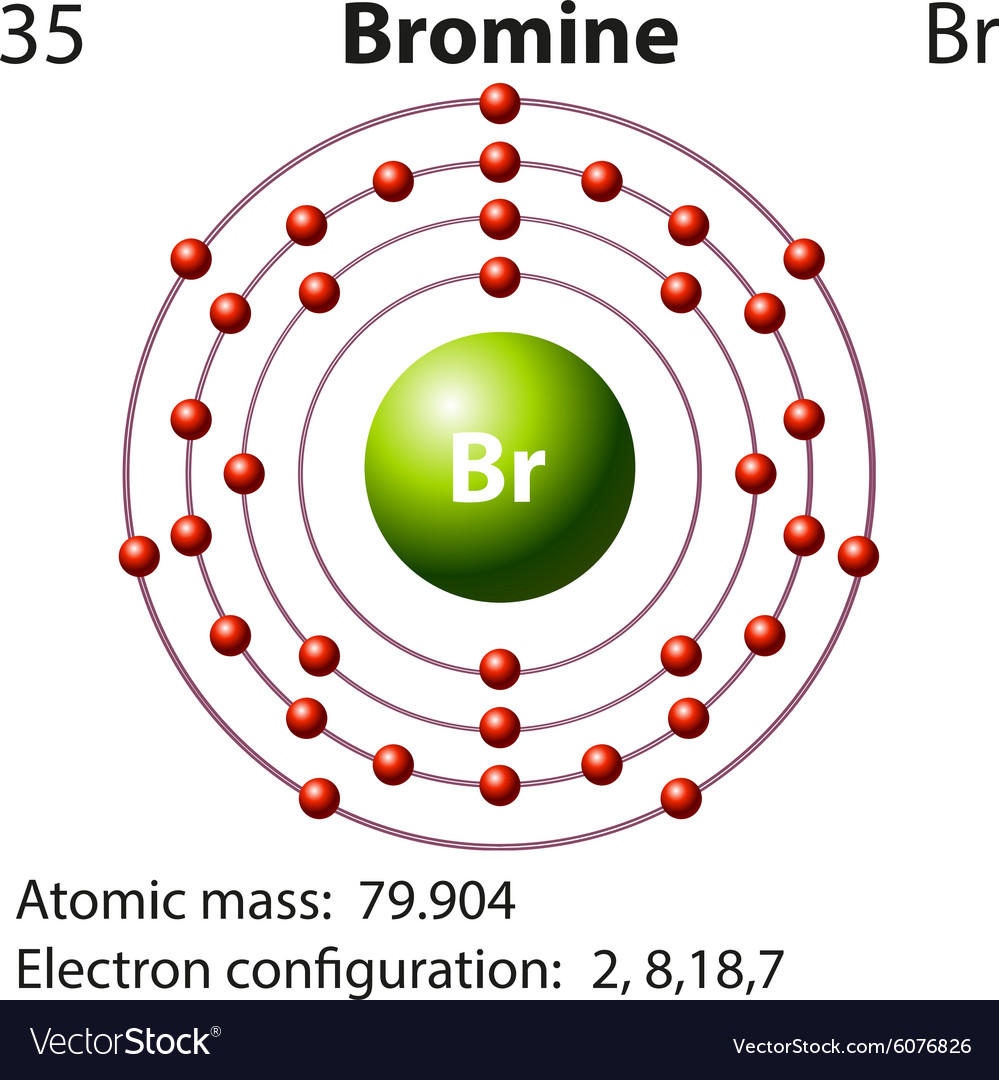
- Atomic Radius: 1.12Å
- Atomic Volume: 23.5cm3/mol
- Covalent Radius: 1.14Å
- Cross Section (Thermal Neutron Capture)σa/barns: 6.8
- Crystal Structure: Orthorhombic
- Electron Configuration:
- 1s2 2s2p6 3s2p6d10 4s2p5
- Electrons per Energy Level: 2,8,18,7
- Shell Model
- Shell Model
- Ionic Radius: 1.96Å
- Filling Orbital: 4p5
- Number of Electrons (with no charge): 35
- Number of Neutrons (most common/stable nuclide): 45
- Number of Protons: 35
- Oxidation States:±1,5
- Valence Electrons: 4s2p5
- Electron Dot Model
- Electron Dot Model
Chemical Properties of Bromine
- Electrochemical Equivalent: 2.9812g/amp-hr
- Electron Work Function:
- Electronegativity: 2.96 (Pauling); 2.74 (Allrod Rochow)
- Heat of Fusion: 5.286kJ/mol
- Incompatibilities:
- combustible organics (sawdust, wood, cotton, straw, etc.), oxidizable material, aqueous ammonia, hydrogen, acetylene, phosphorus, aluminum, titanium, mercury, potassium, other metals.
- Ionization Potential
- First: 11.814
- Second: 21.8
- Third: 36
- Valence Electron Potential (-eV): -7.35
Physical Properties of Bromine
- Atomic Mass Average: 79.904
- Boiling Point: 332.4K 59.25°C 138.65°F
- Coefficient of lineal thermal expansion/K-1: N/A
- Conductivity
- Electrical:
Thermal: 0.00122 W/cmK
- Electrical:
- Density: 3.119g/cc @ 300K
- Description:
- Heavy, red-brown, fuming liquid with a choking, irritating odor; causes tears
- Elastic Modulus:
- Bulk: 1.9/GPa
- Enthalpy of Atomization: 111.7 kJ/mole @ 25°C
- Enthalpy of Fusion: 5.29 kJ/mole
- Enthalpy of Vaporization: 15.46 kJ/mole
- Flammablity Class: Noncombustible Liquid
- Freezing Point:see melting point
- Heat of Vaporization: 15.438kJ/mol
- Melting Point: 266.05K -7.1°C 19.2°F
- Molar Volume: 25.62 cm3/mole
- Optical Refractive Index: 1.001132
- Physical State (at 20°C & 1atm): Liquid
- Realitive Gas Density (Air=1) = 5.51
- Specific Heat: 0.473J/gK
- Vapor Pressure = 5800Pa@-7.1°C
Regulatory / Health
- CAS Number
- 7726-95-6
- UN/NA ID and ERG Guide Number
- 1744 / 154
- RTECS: EF9100000
- NFPA 704
- Health: 4
- Fire:
- Reactivity:
- Special Hazard:
- OSHAPermissible Exposure Limit (PEL)
- 1 ppm = 6.54mg/m3 @ 25°C & 1 atm
- TWA: 0.1 ppm
- OSHA PEL Vacated 1989
- TWA: 0.1 ppm
- STEL: 0.3 ppm
- NIOSHRecommended Exposure Limit (REL)
- TWA: 0.1 ppm
- STEL: 0.3 ppm
- IDLH: 3 ppm
- Routes of Exposure: Inhalation; Ingestion; Skin and/or eye contact
- Target Organs: Respiratory system, eyes, central nervous system, skin
- Levels In Humans:
Note: this data represents naturally occuring levels of elements in the typical human, it DOES NOT represent recommended daily allowances.- Blood/mg dm-3: 4.7
- Bone/p.p.m: 6.7
- Liver/p.p.m: 0.2-7
- Muscle/p.p.m: 7.7
- Daily Dietary Intake: 0.8-24 mg
- Total Mass In Avg. 70kg human: 260 mg
Who / Where / When / How
- Discoverer: Antoine J. Balard/ C. Löwig
- Discovery Location: Montpellier France/Heidelberg Germany
- Discovery Year: 1826
- Name Origin:
- Greek: brômos (stench).
- Abundance of Bromine:
- Earth's Crust/p.p.m.: 0.37
- Seawater/p.p.m.: 65
- Atmosphere/p.p.m.: N/A
- Sun (Relative to H=1E12): N/A
- Sources of Bromine:
- Occurs in compounds in sea water, Dead Sea, natural brines and salt-lake evaporates. World wide production estimated to be around 330,000 tons per year. Main mining areas are USA, Israel, UK, Russia, France and Japan.
- Uses of Bromine:
- Used for water purification (swimming pools), manufacture of ethylene dibromide (anti-knocking gasoline), bleaching, organic synthesis, solvent, analytical reagent, fire retardant for plastics, pharmaceuticals, shrink-proofing wool.
- Additional Notes:
Bromine Menu
Bromine Atom Map
- Bromine Page One
- Bromine Page Two
- Bromine Page Three
References
A list of reference sources used to compile the data provided on our periodic table of elements can be found on the main periodic table page.
Related Resources
Bromine Atomic Weight
- Anatomy of the Atom
Answers many questions regarding the structure of atoms. - Molarity, Molality and Normality
Introduces stoichiometry and explains the differences between molarity, molality and normality. - Molar Mass Calculations and Javascript Calculator
Molar mass calculations are explained and there is a JavaScript calculator to aid calculations. - Chemical Database
This database focuses on the most common chemical compounds used in the home and industry.
Citing this page
If you need to cite this page, you can copy this text:
Kenneth Barbalace. Periodic Table of Elements - Bromine - Br. EnvironmentalChemistry.com. 1995 - 2021. Accessed on-line: 4/25/2021
https://EnvironmentalChemistry.com/yogi/periodic/Br.html
.
Bromine Atomic Mass
Linking to this page
If you would like to link to this page from your website, blog, etc., copy and paste this link code (in red) and modify it to suit your needs:
<a href='https://EnvironmentalChemistry.com/yogi/periodic/Br.html'>echo Periodic Table of Elements: Bromine - Br (EnvironmentalChemistry.com)</a>- Comprehensive information for the element Bromine - Br is provided by this page including scores of properties, element names in many languages, most known nuclides and technical terms are linked to their definitions.
.
Bromine Atomic Number
NOTICE: While linking to articles is encouraged, OUR ARTICLES MAY NOT BE COPIED TO OR REPUBLISHED ON ANOTHER WEBSITE UNDER ANY CIRCUMSTANCES.
Bromine Atomic Number
PLEASE, if you like an article we published simply link to it on our website do not republish it.
